
How to Create the Perfect SEO Strategy for 2022 [+ Template] – In this article I share a step-by-step process for creating the perfect SEO strategy for your website.
By reading the article you will learn about the basics of SEO, what an SEO strategy is and how to set up your website or blog for success on Google.
If you are a brand looking for some help with your SEO, please make sure you check our SEO Strategy services.
Let’s start talking about SEO strategy by covering the basics.
SEO Strategy: the Basics
What is a Search Engine?
A search engine is a large database of web pages and resources like image, video and audio files.
Google is the most popular and used search engines. So when you think about a search engine is, think ‘Google’.
Other search engines you might know are Yahoo!, Bing, DuckDuckGo.
How Does a Search Engine Work?
A search engine has four main functions:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Ranking
- Returning
What Does Crawling a Web Page Mean?
Crawling a web page means visiting and fetching a web page with the purpose of adding it to the search engine database.
What Does Indexing a Web Page Mean?
Indexing a web page means adding it to the search engine database.
What Does Ranking a Web Page Mean?
Ranking a web page means ordering the position of a web page for a given search query in the search engine results pages.
What Does Returning a Web Page Mean?
Returning a web page means showing a given web page in the search engine results pages.
How Does a Search Engine Rank a Web Page?
A search engine establishes and follows a number of rules for ranking web pages and resources. These rules are called ranking factors.
Each search engine uses its own ranking factors, although many of them overlap (for example, the title tag is an important ranking factor for the majority of search engines).
The combination of these ranking factors results in the ranking of a web page for a given search query.
The ranking doesn’t happen in real time but it’s pre-established within the database through an algorithm.
Why Some Pages Rank Better than Others?
A search engine ranks a web page based on how relevant its content is for a given search query and how optimised for search engines (= how compliant the page is with its ranking factors).
What Does It Mean that a Page is Optimised for Search Engines?
It means that the web page is compliant with a number of search engine rules (ranking factors).
This is generally the result of some Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) work.
What is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimisation and it’s an online marketing tactic aiming at improving the ranking, visibility and traffic of web pages on search engines like Google.
SEO is traditionally broken down into:
- On-Page (or On-Site)
- Off-Page (or Off-Site)
- Technical SEO
What is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO is the practice of optimising all the elements that are visible on a given web page.
Some of the elements on a web page that you can optimise include:
- Page Title
- (Meta) Description
- Text Content
- Sub-Headings
- Images
- Page Load Speed
What is Off-Page SEO?
Off-Page SEO is the practice of increasing the authority of a given web page by generating backlinks on third party websites.
A backlink is a hyperlink from another website.
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the practice of optimising all the elements of a web page that are not immediately visible.
Some of the elements that you can optimise are:
- Sitemap
- Robots.txt
- 404 Errors
- Broken Links
Most of the times, an SEO strategy is a combination of On-Page, Off-Page and Technical SEO.
Before deep-diving into creating an SEO strategy, I want to make sure you are familiar with the concept of ‘strategy’.
Strategy, Goals, Objectives and Tactics
What is a Strategy?
A strategy is a number of steps within a plan of action to achieve a given goal.
It’s the roadmap between your current performance, which will be used as a starting point or baseline, and the result you want to achieve (your goal).
A strategy is typically broken down into:
- Goals
- Objectives
- Tactics
What is a Goal?
A goal is a generic result that people and organisations set to achieve in the future.
Some of the typical goals in Digital Marketing include:
- Increase sales
- Increase brand awareness
- Increase engagement
Each goal is broken down into objectives.
What is an Objective?
An objective is a defined result that supports the main goal, typically to be reached within a given timeframe.
The ideal objective within a goal is SMART:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Realistic (or Relevant)
- Time-Bound
For example, if the main goal were to increase brand awareness, an objective could be increase website traffic by X by the end of Month Y.
What is a Tactic?
A tactic is a specific and strategic action aiming at helping with achieving an objective.
For instance, one tactic for the example above (‘increase website visits’) could be the creation of a detailed content plan to attract more visitors to your blog.
How to Measure the Success of a Strategy?
The success of a strategy is measured on whether the main goal was achieved or not.
The achievement of the goal depends on the agreed objectives, which are typically measured by choosing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
The KPIs are strictly related to the main goal and its corresponding objective.
I am writing about the most common goals and objectives later in this article. For now, let’s say that one KPI for our sample objective could be the number of sessions to your website.
I am hoping everybody is now familiar with these marketing concepts.
Let’s then deep-dive into the main focus of this article, creating an SEO strategy, by asking a simple question: what is an SEO strategy?
What is an SEO Strategy?
An SEO strategy (also known as Search Engine Optimisation strategy) is a number of steps within a plan to achieve a given SEO goal.
What Is the Best SEO Strategy?
The best SEO strategy is the one that helps you achieve your SEO goals in the most efficient, cost-effective and timely way.
Why Is This the Best SEO Strategy?
The SEO strategy I am recommending is based on a combination of:
- Experience
- Industry practices
- Google patents.
Best SEO Strategy in My Experience
Without mention any client, I am using this SEO strategy for my website with decent results.
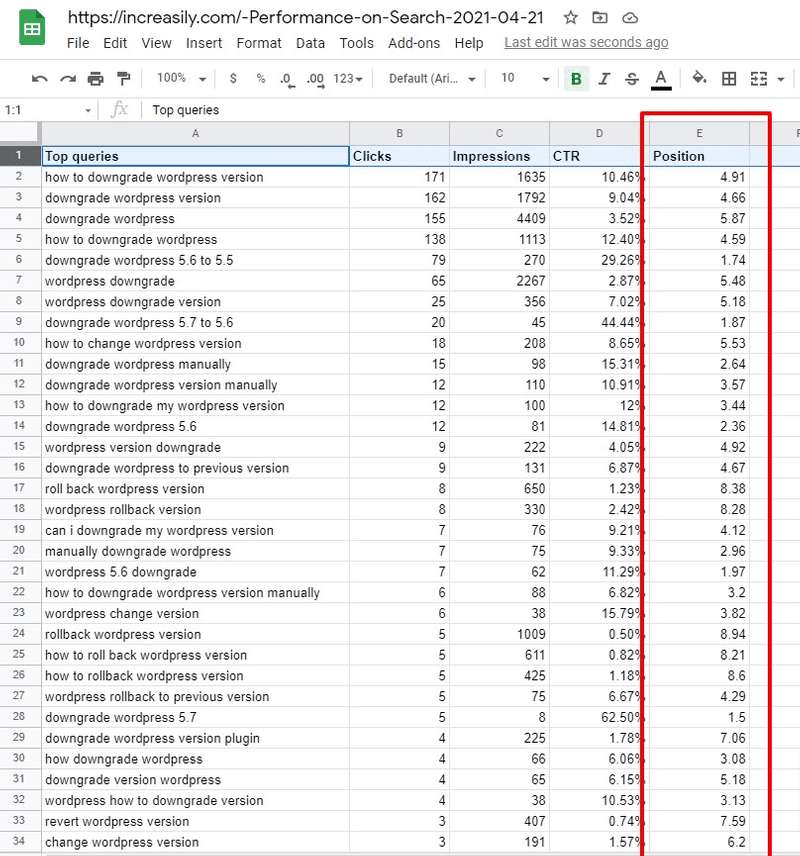
In the screenshots below, which are taken from Google Search Console, I am showing you how I managed to rank for highly-relevant keywords concerning respectively WordPress and Shopify.
As you can see, my website ranks very high for long-tail keywords related to the primary topic.
Rankings from SEO Strategy with ‘WordPress’ as a Primary Topic
Rankings from SEO Strategy with ‘Shopify’ as a Primary Topic
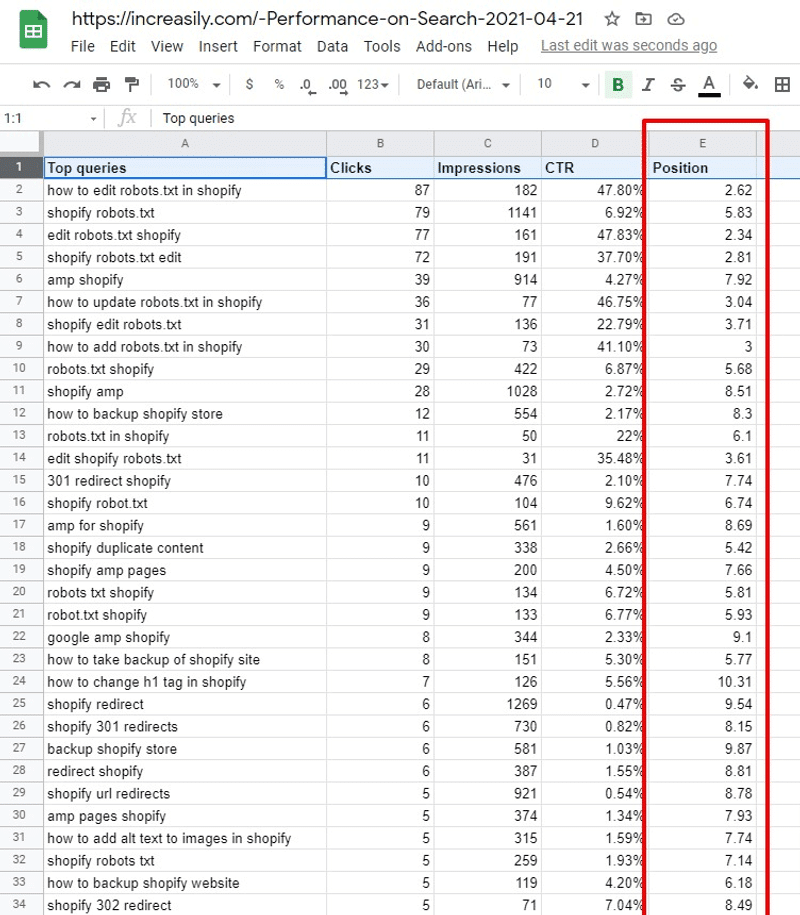
If you are still unsure, you might want to check what other people say about applying this SEO strategy.
Best SEO Strategy According to Industry Practice
Variations of this SEO strategy have been used by some of the most respectable SEO experts:
- Brian Dean from Backlinko recommends this SEO strategy in this article
- The people at Hubspot were the first to discover the potential of this SEO strategy
- Search Engine Journal also writes about this SEO strategy in this article
Additionally, Google indirectly embraces this SEO strategy by way of looking at its patents.
Best SEO Strategy According to Google Patents
One of the most important Google patents in recent years is the so-called ‘Content Clustering’ patent:
The patent describes grouping websites and pages by topic and creating something that can be described as expert clusters. Content from these clusters is then given priority when serving search results for a related query (source: link-assistant.com).
The implications for your SEO strategy are that the more you establish and focus on a primary topic, the higher the chances of ranking well on Google.
Another patens is about ‘Document scoring based on document inception date‘. Translated, this means that Google gives priority to fresh and recent content over old and static one.
There are more patents worth considering. If you are interested, I recommend this article on Google patents by the guys at Link-Assistant.com.
For now, I hope this is enough to convince you about the proven efficacy of the SEO strategy that we are now going to create together.
How to Create an SEO Strategy
I don’t believe there is only one way to create an SEO strategy. The template I am proposing now is one that works for me. I also use it with my clients.
I would recommend using it as a starting point or baseline and add / remove based on the SEO project you are working on.
When it comes to creating an SEO strategy, I consider five steps, in ascending order:
- SEO Audit of Your Website
- SEO Audit of Your Competitors’ [OPTIONAL]
- Set Goals, Objectives and KPIs
- List Your Primary Topics, Services or Products (and Secondary Sub-Topics)
- Identify Your Audience
- Create a Blog and Write about Your Secondary Topics
- Create a Content Cluster through Internal Linking
- Monitor, Optimise and Report
1. SEO Audit of Your Website
Any SEO strategy starts with an assessment of the current performance. In SEO this is typically done by checking how your website currently performs in the three main areas mentioned before:
- On-Page SEO
- Off-Page SEO
- Technical SEO
Depending on your level of expertise and scope of the project, you might go for a DYI SEO audit, in which you consolidate the findings from several SEO tools, or you could use just one of the many SEO Audit tools available online.
I would suggest the DYI SEO audit for the advanced user, while using a single SEO tool might be better suited for beginners and average business owners.
Single SEO Audit Tool
The main benefit of using such tools is that they consolidate in one, visual report the findings from On-Page, Off-Page and Technical SEO.
All the tools are free. Some tools have limitations such as limited number of reports you can get. Other tools require that you create an account.
Disclaimer about the Tools Used
It’s worth mentioning that for the purpose of this article I am only looking at a tiny fractions of what these tools can do. This is true in relation to SEO metrics but also marketing in general.
It’s also worth mentioning that I am not affiliated with any of the tools mentioned below. These are just the tools that I use for my work.
List of Free Online SEO Tools
The following is a list of selected free online SEO tools for you to consider:
Ahref Webmaster Tools (for advanced users)
Main Features
- SEO issues monitoring
- Monitoring of 100+ SEO issues
- Detailed advice on how to fix each issue
- It shows all known links
- Domain & page-level SEO metrics
- Broken links data for internal and external links
- Link type data (nofollow, UGC, sponsored)
- It shows all known keywords
- SEO metrics for pages and keywords
- SERP snapshot with competitive data
- SERP features for every keyword
Hubspot Website Grader
Main Features
- It gives you a quick overview of your website performance in seconds
- It analyses the following areas: performance, SEO, mobile, and security
- Very visual reporting
Seoptimer
Main Features
- Comprehensive website audit including SEO, usability, performance, social, security
- Simple DIY SEO tool, ideal for the small business owner
- It gives you actionable recommendations
SEO Site Checkup
Main Features
- Trusted by over 15,000 webmasters, small business owners & SEO agencies in over 120 countries
- A set of SEO tools to help you understand your website from a search engine’s perspective
- It lets you know of any problems or technical shortcomings in your website that may be hurting your search engine rankings
- The free version offers only one website check per day
Other online free SEO audit tools you might want to consider:
List of Free SEO Browser Extensions
Sometime you might want to audit the SEO of a given website right away, while you are looking at it.
If that’s the case, you might want to consider some of these free SEO browser extensions:
- SEOquake
- Browseo
- The Tech SEO (I am using this one)
If the scope of your project goes beyond what’s covered by these reporting tools, then you might want to consider a DIY SEO audit to start off your SEO strategy. Let’s see how!
DIY SEO Audit
I call it DIY because in this case you will be combining and consolidating the findings from more than on free SEO tool.
Every DIY SEO audit is by definition custom as it is strictly dependent on the nature and scope of the project and website.
Having said that, I am listing below the template that I use for my SEO projects and clients. This is usually broken down into the following areas (each area corresponds to a slide of my presentation):
On-Page SEO
- On-Page Optimisation
- Keyword Ranking
- Layout
- Page Load Speed
Off-Page SEO
- Backlink Profile
Technical SEO
- Indexation and Crawlability
- Site Structure and Hierarchy
- Broken Links and Code Errors
On-Page Optimisation
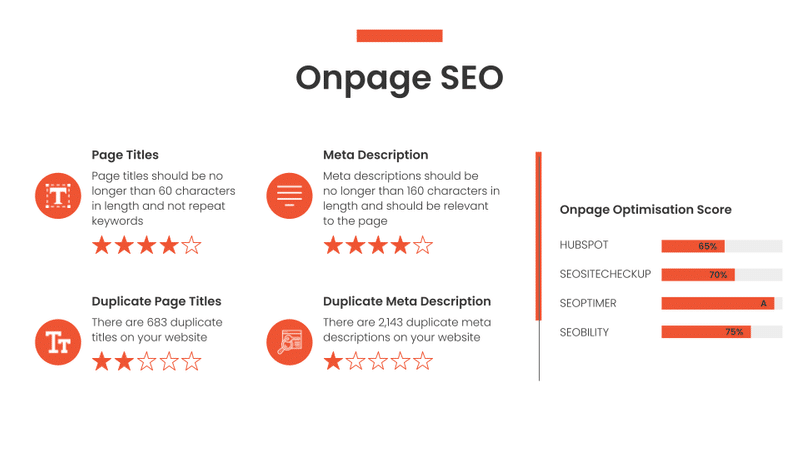
On-Page optimisation is about how well-optimised for Google your page is.
If you recall from what I wrote earlier in the article, optimised means how compliant a given web page is with the search engine rules.
In this slide I give a quick overview and score to the two main elements of any web page: title tag and meta description.
What is the Title Tag?
The Title Tag, also known as SEO Title or Meta Title, is the title of a web page that is displayed in the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
It is not to be confused with the Page Title that is visible on the actual web page, although there is often an overlap between the two.
The SEO Title is arguably one of the most important ranking factors of on-page optimisation.
The function of the SEO Title is to let both visitors and Google know what the corresponding web page is about.
For potential visitors, the SEO Title is the most prominent element they will see on the SERPs.
For Google and other search engines, the SEO Title is one of the main elements used to understand what topic or keyword theme a web page is about.
What is the Meta Description?
The Meta Description is a short excerpt from a web page that is displayed in the SERP.
The Meta Description has an indirect impact on the rankings of your web page.
Although Google doesn’t consider it as a ranking factor anymore, it can indirectly impact current ranking factors and page experience metrics such as Click-Through-Rate, Dwell Time and Bounce Rate.
Note from the author: it’s not clear whether metrics such as bounce rate or dwell-time are being considered as ranking factors by Google or not.
In addition to checking their level of optimisation, I also check for duplicate title tags and meta descriptions.
In this context, duplicate means an identical title tag and / or meta description being used for more than one web page.
To support my findings, I test the homepage of each website against four free SEO audit tools from the ones I listed before and report the corresponding overall score.
How to Audit the On-Page Optimisation of a Website (Using Multiple Tools):
- Visit:
- Hubspot Website Grader
- Seoptimer
- Seositecheckup
- Seoability
- Enter the domain of the website you want to audit
- Click on Analyze or Audit
Keyword Ranking
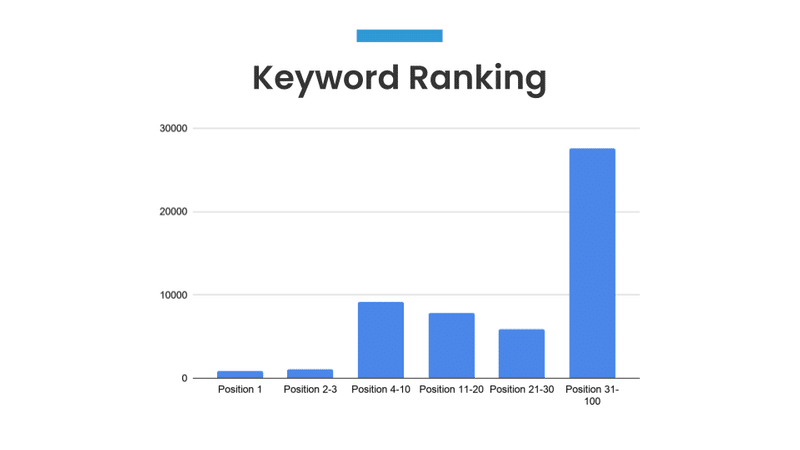
Depending on the number of keywords being considered, I either show the rankings for 4-5 main keyword phrases on Google (Bing and Yahoo! on occasion) or I show the total number of keywords the website ranks for and corresponding positions.
To make sure the slide is clearly understood: Position is the ranking in Google search results. The numbers of the vertical axis are the number of keywords the website ranks for.
For example, according to the chart this website ranks in position 4-10 (first page of Google) for nearly 10,000 keyword phrases.
How to Discover the Overall Number of Keywords a Website Ranks for (on Seoptimer):
For this slide, I use the Seoptimer mentioned earlier in this article:
- Visit seoptimer.com
- Enter the domain you want to audit
- Click on Audit
- Scroll down to the Keyword Ranking section
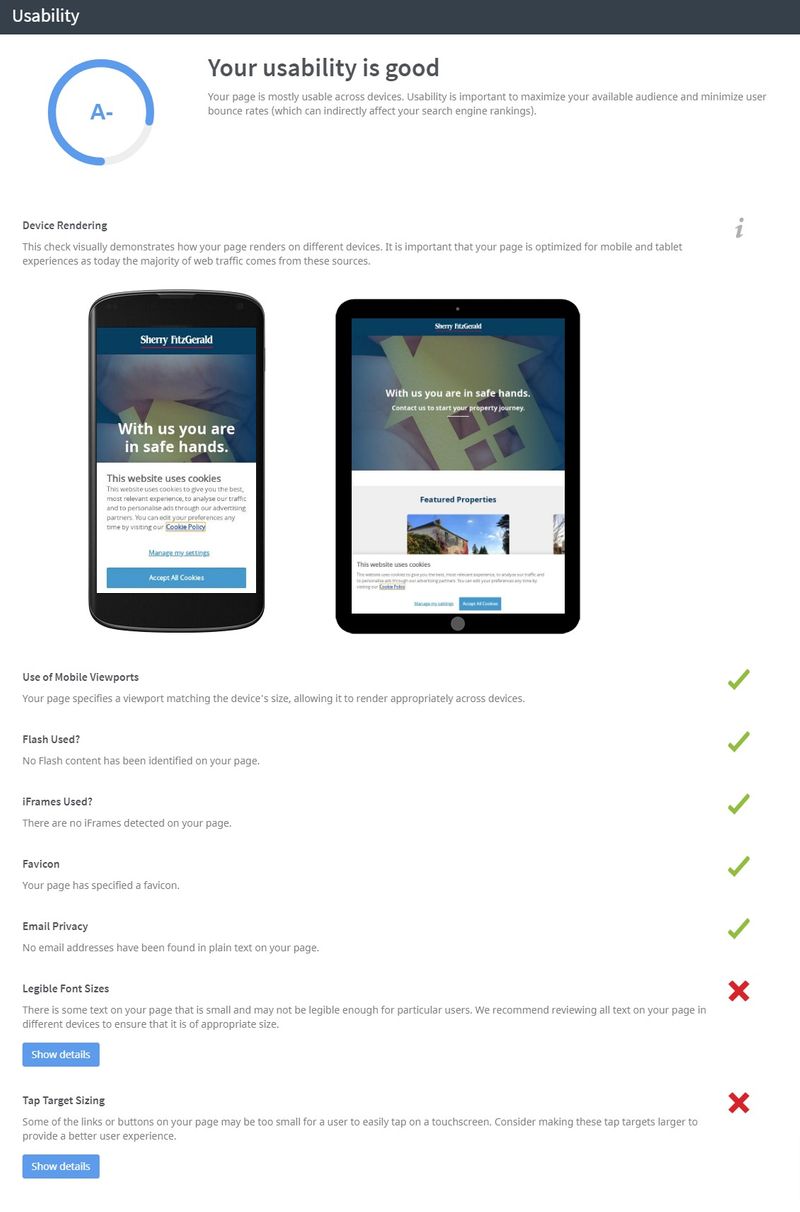
Responsive Layout (Mobile Friendly)

In the Responsive Layout part of my DIY SEO Audit, I mostly check how usable and responsive the layout is.
Specifically, I check for issues with the following elements:
- Responsive Design
- Use of Viewport
- Tap Target Sizing
- Flash or Iframes
This slide is generally built by using data taken from Seoptimer too.
How to Check If Your Website is Mobile Friendly (on Seoptimer):
- Visit Seoptimer.com
- Enter the domain you want to audit
- Click on Audit
- Scroll down to the Usability section
Page Load Speed
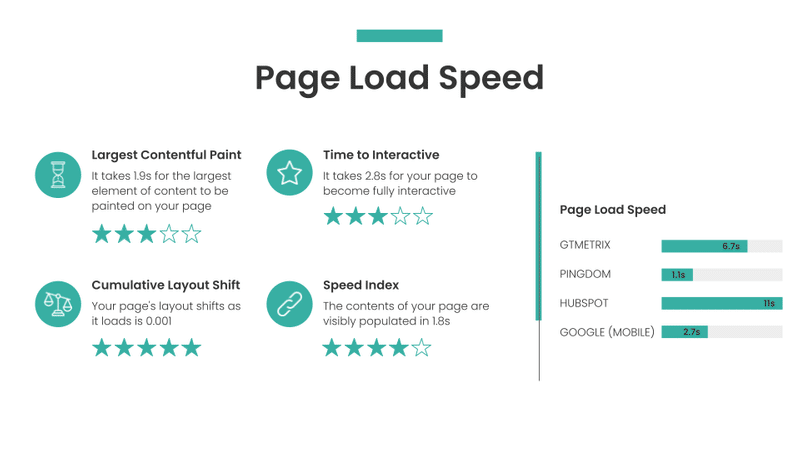
If you have been paying attention to the chatter within the SEO community for the past few months, the words ‘Core Web Vitals’ will sound familiar to you.
They are a number of metrics selected by Google that capture the experience of the user on a given web page.
Most of the metrics have to do with how fast your web page takes to load on a given device.
After announcing page experience metrics in May 2020 and introducing Core Web Vitals in November 2020, Google will officially consider them as a new ranking factor starting May 2021.
For now, it’s enough to say that the faster your web page loads, the higher the chances of ranking high on Google Search.
To test a given web page for speed, I use the following tools:
- Gtmetrix.com
- Pingdom Tools
- Hubspot Website Grader (also used for the On-Page Optimisation slide)
- Test My Site with Google
How to Test a Website Page Load Speed (on Gtmetrix.com):
- Visit Gtmetrix.com
- Enter the domain of the website you want to audit for page load speed
- Click on Analyze
I then go into detail and test the following Core Web Vitals against Google’s benchmarks:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- Time to Interactive (TTI)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- Speed Index
What is the Largest Contentful Paint?
Large Contentful Paint (LCP) measures the time it takes for the largest element on the page to be made visible
What is the Time to Interactive?
TTI measures how long it takes a page to become fully interactive.
What is the Cumulative Layout Shift?
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures the sum of all unexpected layout shifts (for example, when an element on a page unexpectedly moves frame) happening on a given page
What is the Speed Index?
Speed Index (SI) is a performance metric that measures how quickly your page is visually complete above-the-fold.
If you want to know more about the topic, make sure you check my article ‘Core Web Vitals and Page Experience FAQs for 2022‘.
Backlink Profile
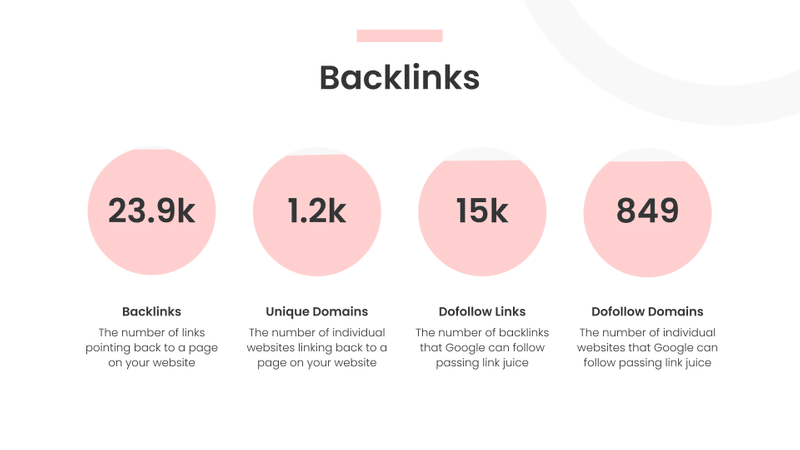
In this slide I take a look at the backlink profile of the website. In brief, I look at the number and quality of backlinks.
A backlink is a hyperlink pointing at your website from another domain.
The main differentiator here is between dofollow and nofollow links.
Dofollow links are links that Google spiders can follow (to see where they lead to) and they pass link juice or link authority. Nofollow links are hyperlinks that are not being followed by Google crawlers.
In the early days of Search Engine Optimization, the higher the number of backlinks pointing at your domain the better the ranking for your website.
Nowadays, the focus is more on the quality of backlinks.
For example, a backlink for high-authority websites such as the Ney York Times, The Guardian or The Irish Times has a lot more value than dozens of low-quality backlinks from websites with low domain authority.
To check the backlink profile of a website, I use SEO Spyglass by Link-Assistant, which is part of the SEO Powersuite.
You can use it for free but if you want to download the report, you need to pay.
How to Check the Number of Backlinks of a Website (with SEO Spyglass):
- Download SEO Spyglass from www.link-assistant.com/seo-spyglass/
- Create a new project
- Enter the domain of the website you want to audit
- Click on Analyze

Indexation and Crawlability
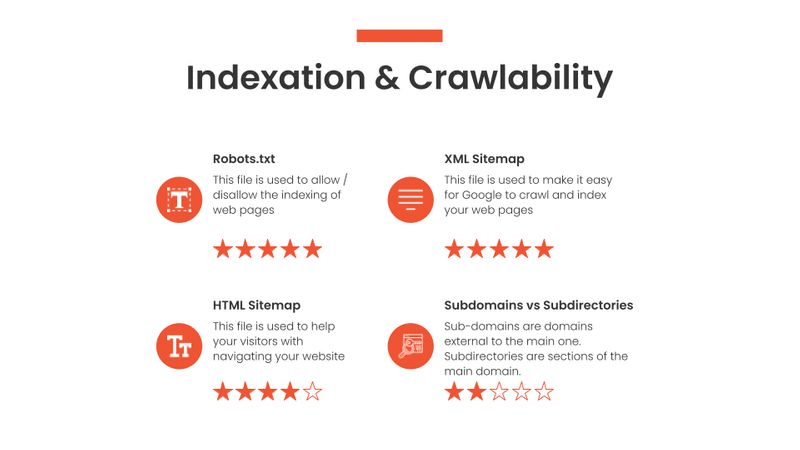
If you have read the section about the SEO basics, by know you know that two key functions of a search engine are crawling and indexing web pages.
For this part, I use another tool from the SEO Powersuite called Website Auditor.
How to Check the a Website for Indexation and Crawlability (with Website Auditor):
- Download Website Auditor from www.link-assistant.com/website-auditor/
- Create a new project
- Enter the domain of the website you want to audit
- Click on Analyze
Here I search for potential issues with crawling and indexing, which can generally be spotted by looking at:
- Robots.txt
- XML Sitemap
- HTML Sitemap
- Site Structure (I have a separate slide for this)
What is the Robots.txt?
The robots.txt is a file in the root directory of your domain instructing search engine crawlers about what pages to crawl.
For example, you might have some admin pages that you don’t want people to find on Google. If that’s the case, here you will add an instruction for Google spiders not to crawl the page.
What is an XML Sitemap?
The XML Sitemap is a hierarchical representation of your site structure. It’s mainly used to help search engines like Google find and index the web pages on your website.
What is a HTML Sitemap?
A HTML Sitemap is a hierarchical representation of your site structure. In this case, the sitemap is mainly used to help visitors find their way around large websites with a high number of pages.
Site Structure and Hierarchy
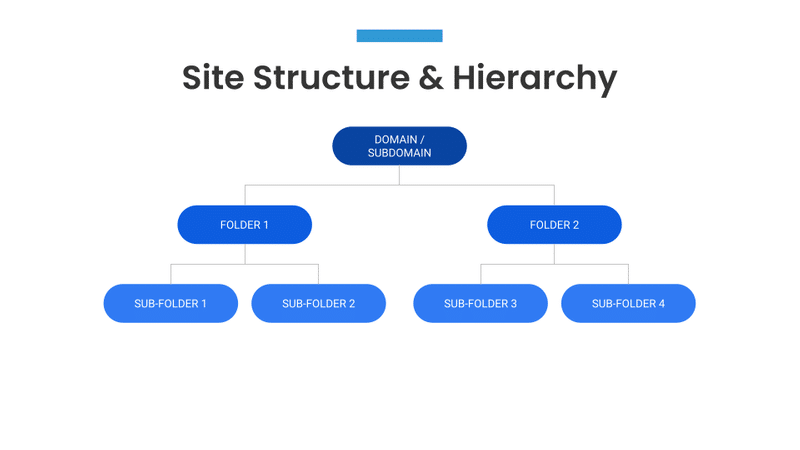
The structure of a website can have a significant impact on its visibility on search engines.
The key differentiator is between a sub-folder OR sub-domain structure:
- Sub-folder = domain.com/folder/sub-folder
- Sub-domain = subdomain.domain.com
If you are interested in the topic, I wrote a very thorough article about the impact of site structure on SEO called ‘Subdomain vs Subdirectory: What SEO Strategy is Best in 2022?
For now, it’s sufficient to point out that Google treats any subdomain as a separate entity from the main domain.
This means that any web page within a sub-domain site structure will not benefit from the authority of the main domain and vice versa.
If you don’t know how much of an impact the site structure could have on your online visibility and traffic, check these two use cases of website moving from subdomain to subdirectory.
The spike represents the volume of traffic from organic search after the move.
I shared this on Twitter about 4 weeks ago, just wanted to re-share as it’s still going up… pic.twitter.com/KVKbdmnLfN
— Andy Chadwick (@digitalquokka) October 29, 2020
Not wanting to start an argument or anything, but here’s what happened when a retail client’s blog was moved from a blog. subdomain onto a /blog/ subfolder 📈 pic.twitter.com/LxMWBV2JAu
— Stephen Kenwright (@stekenwright) October 20, 2020
How to Check the Site Structure of a Website (with Website Auditor):
- Download Website Auditor from www.link-assistant.com/website-auditor/
- Create a new project
- Enter the domain of the website you want to audit
- Click on Analyze
Broken Links and Code Errors
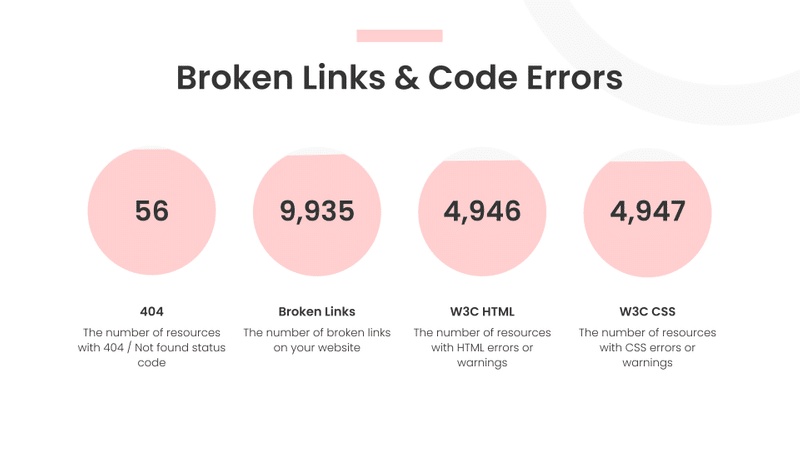
The last slide of my DIY SEO audit is about identifying broken links and code errors. In this slide I look at:
- 404s
- Broken Links
- HTML errors and warnings
- CSS errors and warnings
It’s not clear how much of an impact these issues have on a website’s visibility and rankings on search engines.
According to logic, a visitor coming across broken links or 404 page not found errors while visiting a website is not getting the ideal page experience that Google would like her to get.
For this reason, such a website is likely to be penalised in some way in terms of lower search engine rankings.
To spot these issues, I use the Website Auditor tool by Link-Assistant that I mentioned earlier in this article.
How to Check a Website for Broken Links and Code Errors (with Website Auditor):
- Download Website Auditor from www.link-assistant.com/website-auditor/
- Create a new project
- Enter the domain of the website you want to audit
- Click on Analyze
Note from the Author
I am aware a number of people use Screaming Frog as their preferred SEO audit tool, especially for the Technical SEO part of the audit. If that’s your case, you can still apply the SEO strategy I am recommending. Most of the data you find in Website Auditor, you can also find in Screaming from.
If you are looking for a guide on how to use Screaming Frog for your SEO audit, you might want to check this article on Search Engine Journal.
To be quite honest, the article goes much deeper in dealing with the Technical side of an SEO audit than my article. I would definitely recommend that you take a look.
To finish off the audit section of the SEO strategy, I am listing below some of the most common issues concerning On-Page, Off-Page and Technical SEO.
On-Page SEO Most Common Issues
These are some of the most common On-Page SEO issues to look for:
- Duplicate title tag
- Duplicate meta description
- Missing title tag
- Missing meta description
- Title tag is too long
- Meta description is too long
- Missing alt text
- Missing H1 tag
- More than one H1 tag on the page
- No sub-headings
- No keywords in sub-headings
- Very low keyword-to-text ratio
- Keyword stuffing
Off-Page SEO Most Common Issues
These are some of the most common Off-Page SEO issues to look for:
- No links
- Low number of links
- Low quality of links
- Links from a handful of domains
- Links from websites that have been penalised by Google
- Links from websites that are at risk of being penalised
- Links from dubious websites
- No links from websites within your geography
Technical SEO Most Common Issues
These are some of the most common Technical SEO issues to look for:
- Missing XML sitemap
- Missing HTML sitemap
- Missing robots.txt file
- Noindex tag applied to the entire website or sections of it
- Pages are slow to load
- Too many 404 Page Not Found errors
- Too many broken links
- No SSL certificate
2. SEO Audit of Your Competitors’ [OPTIONAL]
Although not always necessary (for example, if you are working in a very specific niche), it’s always a good idea to do an SEO audit of your competitors’ websites.
You will often find insights and learnings that you can apply and implement in your own SEO strategy.
For example, you might find that a competitor’s page that ranks well for one of the keywords you are interested in has a backlink from a website that you know. You might then go and try to get that backlink for your website too.
If you are using a suite of tools like SEO Powersuite, you can add as many competitors as you like and cross-check how they compare to your website’s performance.
3. Set Goals, Objectives and KPIs
Once you have established your current performance, which is also your starting point, it’s now time to set goals, objectives, tactics and KPIs.
You should know by know the difference between goals, objectives and KPIs. Below I am listing some of the most commonly-used SEO goals and their corresponding objectives.
Most Common SEO Goals (and How to Choose Them)
There are several SEO goals you can choose from for your SEO strategy. Choosing the right SEO goal depends on the type of website or business you are running.
For example, if you are managing a news website whose revenue model is based on displaying ads, you might want to focus on driving as much traffic as possible to your website.
Vice versa, if you have a brochure website showcasing your company’s services, a suitable SEO goal could be increasing the number of leads.
Below you can find three of the most common SEO goals with corresponding SEO objectives:
a. SEO Goal and Objectives: Traffic
Choose traffic as a goal for your SEO strategy if your website can monetise traffic without the need for any action or transaction from your visitors.
The most common SEO objectives supporting a traffic goal are:
- Increase the number of sessions
- Improve your rankings
- Diversify your traffic sources
- Capture more feature snippets
List of KPIs for Traffic Objectives
The following is a sample list of KPIs supporting traffic objectives:
- Number of sessions from organic search
- Click-Through-Rate
- Ranking for given keywords
b. SEO Goal and Objectives: Sales
Choose sales as a goal for your SEO strategy if you have a brochure website, showcasing your services, or an online shop selling your products on the internet.
The most common SEO objectives supporting a sales goal are:
- Increase leads
- Increase sales
- Increase conversions
There are also some objectives that indirectly will support your sales goal. These are:
- Improve page load speed
- Decrease your bounce rate
- Increase dwell time
List of KPIs for Sales Objectives
The following is a sample list of KPIs supporting sales objectives:
- Number of sales
- Number of leads
- Number of events (Google Analytics)
- Number of sessions
- Number of page views per session
- Conversion Rate
- Cost per Sale
- Cost per Lead
- Checkout Abandonment Rate
c. SEO Goal and Objectives: Branding
Choose branding as a goal for your SEO strategy if you want to increase the online reputation for your brand.
Some of the SEO objectives for branding goals are:
- Increase the quality of your backlinks
- Increase your domain authority
List of KPIs for Branding Objectives
The following is a sample list of KPIs supporting branding objectives:
- Number of backlinks
- Domain Authority
- Domain authority of your backlinks
- Number of guest posts
- Number of internal links
- Number of external links
After agreeing and establishing your goals, objectives and KPIs is now time to apply the SEO tactics I am recommending and come up with a list of your website’s primary and secondary topics.
3. List Your Website’s Primary (and Secondary) Topics / Services / Products
A website is generally about one or more:
- Topics
- Services
- Products
Identifying the primary topics / services / products for your website is the next step in the drafting of your SEO strategy.
How to Find Your Website’s Primary Topic
![]()
To identify your website’s primary topic:
- Think about a short word that best describes the main topic of the site (for example, if the website is about vegetarian dishes, ‘vegetarian recipes’ might be a main topic keyword)
- Next, use a free keyword tool to check the average search volume for your keyword (in this example, I am using Wordtracker.com)
The search volume is the number of times that keyword has been used within a given timeframe. It gives you an idea on how popular the said keyword is.
It’s very likely that the higher the search volume, the higher the competition for a given keyword is.
Choosing a more or less competitive keyword depends on several factors. Ideally, you want to choose a keyword that is competitive but not so much.
For a new website, it’s probably safer to go for keywords with low competition.
In any case, I would not recommend choosing a main topic keyword whose search volume is lower than 1,000 searches per month.
Note from the author: I recommend putting the search volume into context. For example, in a country like the United States or India 1,000 searches per month is a very low search volume.
Vice versa, in a country like Ireland this search volume could be more than acceptable, especially for very niche topics, products or services.
Once you find your main topics, try breaking down the primary topic into 5-10 secondary topics.
How to Find Your Website’s Secondary Topics
![]()
To find secondary topics for your website:
- Let’s go back to our keyword search volume tool (in my case, Wordtracker.com)
- Pick up to 10 secondary topics from either main table or Suggestions table on the left
The secondary topics will be the content you will mostly write about in your blog.
Yes, nowadays a blog is what you need to get the most out of any SEO strategy.
Before that, you need to make sure you know who the articles are going to be for and identify your audience.
5. Identify Your Audience
To identify the audience of your SEO strategy, ask yourself these questions:
- Who are your customers?
- What problem(s) do they have?
- How are you going to help?
If you don’t have the answer for one ore more of the questions above, you might need to create a marketing persona.
How to Create a Marketing Persona
If you are working for a relatively structured company, chances are you have one or more marketing personas.
A marketing persona is a portrait of your ideal customer(s). If you don’t have a marketing persona template, you can create a simple one to start with.
The more specific you are with describing your marketing persona, the better SEO strategy you can put in place.
Some of the information you might want to include in your marketing persona template are:
- Age
- Location
- Language
- Spending power and patterns
- Interests
- Content they like
- Challenges
- Stage of life
How to Identify Your Audience’s Challenges
To identify your audience challenges, you can:
- Ask them directly via email survey or phone calls
- Ask your sales or customer teams
- Read the comments on your social media channels
- Read statistics and data
Once you get to know what your customers’ main problems are, the final question is about how you are going to help them through your content.
How to Write Blog Articles That Help Your Audience
To make sure you are writing blog posts that help your audience, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your article unique?
- Is your blog content better than what’s currently available?
- Is it complete?
There are many more questions you can ask regarding your audience, their challenges and how you are going to help.
I will leave this open to your and your curiosity.
One you are done with this task, it is now time to continue with your SEO strategy by creating your blog and start writing!
6. Create a Blog and Write about Your Secondary Topics
The next step of your SEO strategy is creating a blog. The blog is going to play a very important role in your SEO strategy.
How Important is a Blog for Your SEO Strategy?
A blog is critical for your SEO strategy because it helps with the following:
- Keeping your content fresh and up to date
- Getting visibility for long-tail keywords
- Allowing internal linking
- Connecting with your audience via comments
Keeping your content fresh and up to date
Most of the content on a given web page rarely changes.
For example, it’s unlikely that content of your About Us page will change regularly, unless your company does too.
This type of content is generally referred to as static content. A static website is a website where the content stays more or less the same.
In turn, blogging regularly can help with generating new content for static websites too. This has a double effect on Google and any other search engine:
- It triggers the indexing of a new page
- It sends a signal about some fresh and up to date content
As you learned earlier, one of the main functions of search engines is to return the most relevant results for a given query.
Relevant means close to the meaning and intent of the search query but ALSO up to date!
In brief, by creating and updating your blog regularly, you send strong signals to Google that your website is alive and has relevant and up to date information ready to be found!
Getting visibility for long-tail keywords
Remember when I searched for the primary topic for a website? In my example I settled for the relatively broad keyword ‘vegetarian recipes’, which has an average search volume of +130,000 per month.
In the screenshot I shared earlier, this keyword showed the second highest score in terms of competition.
This means that the keyword is very competitive (= many other website are trying to rank for the same keyword). This also means that it’s going to be difficult to rank for this keyword on Google.
That’s where long-tail keywords come into play.
What Are Long-Tail Keywords?
Long-tail keywords are keywords phrases made of more than 4-5 keywords. They generally have a relatively low volume and definitely lower than broad keywords.
In our example, ‘vegetarian recipes’ (+130,000 searches per month) is considered a broad keyword.
On the other hand, a search query like ‘What are the best vegetarian gluten free recipes?’ is considered a long-tail keyword whose search volume is definitely lower than the broad one.
Why should you bother with long-tail keywords if their search volume is much lower?
Well, first of all long-tail keywords represent something like 92% of all the search queries (source: ahrefs.com).
Secondly, long-tail keywords are generally used by users who are much closer to converting than those who are simply ‘searching’.
In the example above, if you were selling a book of vegetarian, gluten free recipes, would you want to show to buyers using ‘vegetarian recipes’ or those searching for ‘what are the best vegetarian gluten free recipes?’.
By regularly writing blog posts you can target less-competitive, more niche and better converting long-tail keywords that are easier to rank for.
Allowing internal linking
I will write about this more in detail in the next section of this article.
For now, you must know that by writing blog post you can put in place an internal linking structure (= hyperlinks within your website) and in so doing creating a topic cluster.
Connecting with your audience via comments
It’s probably worth mentioning that another difference between static content, or your average web page, which has no comment functionality, and blog posts.
Naturally, you can disable the comments but if you leave them on you will have a chance to connect with your audience.
In my own experience, the comment section of the blog can be used to get additional questions that the article might have missed or not covered in depth.
How to Create a Blog
Nowadays, most website platforms come with a blog section by default.
If you are using WordPress, Shopify, Wix or Squarespace or any other Content Management Systems (CMSs), chances are you already have a blog (you might need to enable it in some cases).
Please note I am not suggesting that you create a blog that is separate from the main website.
In my experience, it’s not rare to come across static websites with a blog hosted on another platform (generally WordPress).
For the same reasons that I mentioned earlier about subdomain vs subdirectory, a blog on a separate platform or as a subdomain (for example, blog.domain.com) would defeat the purpose of your SEO strategy.
How to Find Ideas for Your Blog
If you have followed the advice given earlier, you have already come up with a list of 5-10 secondary topics.
It’s now time to put those topics to work and start putting together ideas for your blog posts.
The task of generating ideas could prove daunting. For this reason, I have two ways to find ideas to write about and I often use them both in conjunction:
What is Feedly?
Feedly is a free content aggregator that works like the old RSS feed. You subscribe to one or more topics or websites. As soon as they publish new content, it will be displayed in your feed.
You can also save content to read later and also create content boards around a particular topic (like you would do in Pinterest).
How to Generate Ideas with Feedly
To generate ideas for a blog post with Feedly:
- Visit feedly.com and login into your account (or create one)
- Select the sources (websites or topics) that are relevant to your primary and secondary topics and to your audience
- Scroll through the articles that you see in your feed (by default you will see Today’s view)
- If there is an article about a topic that you feel it’s important for your audience, save it to the corresponding board by clicking on the star icon (if there are no board, you can create one or more)
- Search for the topic online to see how many articles are out there (= competition)
- Ask yourself if you can add something new, unique or simply better to the conversation
- Assuming the answer is yes, start planning your article
I mostly use Feedly for time-sensitive content. For example, a Google search algorithm update.
What is Usetopic Blog Idea Generator?
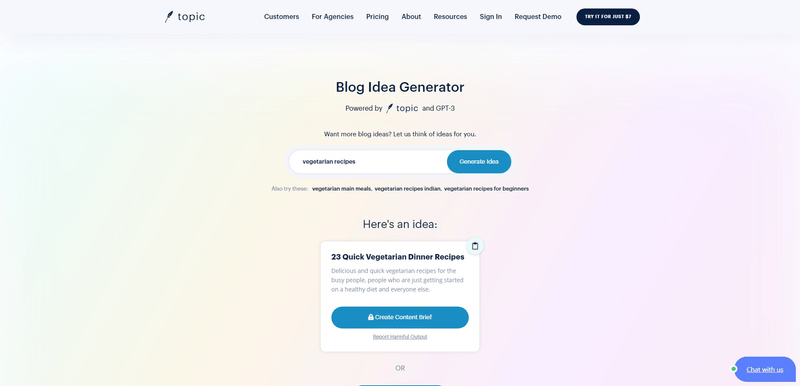
It’s a free online tool to help you generate ideas for your blog posts based on your chosen topics.
How to Generate Ideas with Usetopic Blog Idea Generator?
To generate ideas with Usetopic Blog Idea Generator:
- Visit www.usetopic.com/blog-idea-generator
- Enter your primary or secondary topic in the field
- Click on Generate Ideas
There are many blog ideas generators online. I like the Usetopic one because it generates ideas that are strictly related to your topic.
In the screenshot above you can see the suggestions I got for ‘vegetarian recipes’.
Hypothetically, I could rank such a blog post for the long-tail keyword ‘quick vegetarian dinner recipes’.
Once you have put together a few ideas, it’s now time to create a content calendar supporting your SEO strategy.
How to Create a Content Calendar for Your SEO Strategy (with Asana)
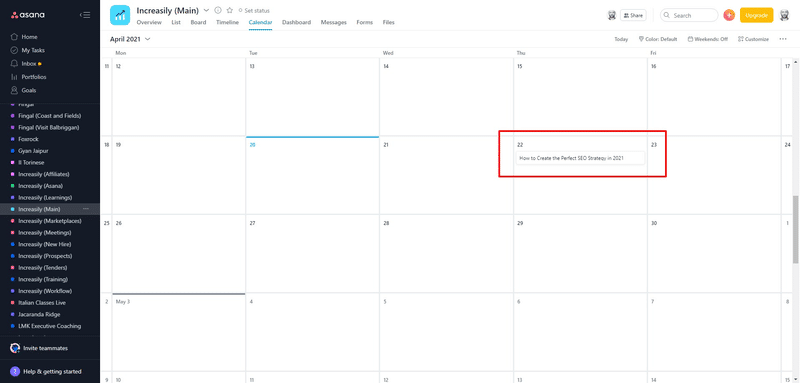
To create a content calendar for your SEO strategy:
- Visit Asana.com
- Log in or sign up for an account (it’s free)
- Create a new project (with the name you like)
- Choose the ‘Calendar’ layout
- Start adding your blog post ideas to your schedule
You can use any calendar tool to keep track of your posting schedule. In this post I am suggesting Asana because it’s the tool we use internally for project management.
After lining up your content calendar, the next step in this SEO strategy is to set up an internal linking structure that will eventually lead to the creation of a content cluster.
7. Create a Content Cluster through Internal Linking
The next step of the SEO strategy is creating a content cluster by way of internal linking.
To do this, you are going to take two steps. You are going to:
- Create a page for your primary topic
- Link your primary and secondary topic pages between each other
1. Create a Page for Your Primary Topic
In this step of your SEO strategy, you are going to create a page for the primary topic of your website.
You can create a page by using any page builder or platform you like (as long as it’s consistent with your website).
In this page, you want to list all your secondary topics.
If your primary topic is ‘vegetarian recipes’, you want to create a page listing all the secondary topics that you have chosen. For example:
- Vegan recipes
- Gluten free recipes
- Veggie burgers
- Vegetarian chili
An so forth.
This is the first step of creating a content cluster for your SEO strategy.
2. Link your primary and secondary topic pages
The second step of creating a content cluster for your SEO strategy is hyperlinking your primary topic page to your secondary topic pages.
This creates what is called a content cluster. A content cluster is a strong signal telling Google (and your visitors) what the primary topic of your website is about.
A topic or content cluster is the subject of one of the most important Google search patents, as you might recall from earlier in this article.
Needless to say, a content cluster is a key element of your SEO strategy.
A link between your primary topic page and your secondary topic pages should be enough to boost your SEO strategy. However, if you want to create an even tighter content cluster, you can take one or more of the following actions:
- From your secondary topic pages or articles, link back to your primary topic one
- Create a category and add both primary and secondary topic pages (in the WordPress and Shopify examples mentioned earlier, this is what I did)
- Create tags for both primary and secondary topics and use them for each one of your pages, where relevant
As soon as this part of your SEO strategy is completed, there is only one thing left to do: launch and measure!
8. Monitor, Optimise and Report
Congratulations for making it this far!
If you have followed all the instructions, you have now created your SEO strategy and set your website or blog up for success on Google!
However, don’t forget that earlier in this article we defined the success of your SEO strategy in terms of achieving the goals, objectives and corresponding KPIs.
For this final part of your SEO strategy, I am recommending that you use three tools:
- Google Analytics
- Google Search Console
- A keyword ranking checker of your choice (I use Rank Tracker)
Disclaimer about the Tools Used
It’s worth mentioning that for the purpose of this article I am only looking at a tiny fractions of what these tools can do. This is true in relation to SEO metrics but also marketing in general.
It’s also worth mentioning that I am not affiliated with any of the tools mentioned below. These are just the tools that I use for my work.
I am going to start by showing you where to look to measure your traffic objectives for your SEO strategy.
How to Monitor Your SEO Strategy with Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a free tool by Google that allows you to discover a lot of date about your visitors.
It’s very easy to install and use. In this SEO strategy, I am going to show you where to check for measuring your traffic objectives.
For this exercise, I am going to use Google Analytics 4, which is slightly different from the previous version.
How to Measure Your SEO Strategy Traffic Objectives with Google Analytics
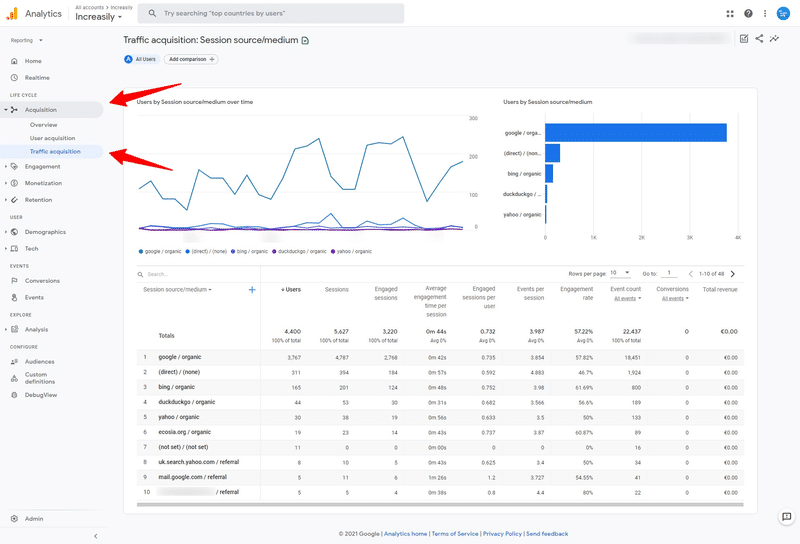
To measure your traffic objectives with Google Analytics:
- Visit analytics.google.com and log in (if you don’t have an account, create one and install the tracking code)
- Select the account and property that you want to monitor
- Click on Acquisition from the left navigation
- Under Acquisition, click on Traffic Acquisition
This section of Google Analytics shows your main traffic sources and mediums. These are generally:
- Organic / Search Engines
- Direct Traffic / Visitors who type your domain in their address bar
- Paid Search / Google Search Ads
- Display / Google Display Ads
- Referral / Traffic following links from other websites
- Social Media / Traffic coming from social media
- Email / Traffic coming from your newsletter
Each column represents a KPI related to your traffic goals: for example, the number of sessions.
You can adjust the report by selecting the preferred timeframe.
You can also export the report from one of the options on the top right.
I can’t stress enough that Google Analytics is huge and what I am proposing here is an ultra-simplification way of checking your traffic goals.
If your goals were more about branding, another tool by Google can help you monitor the number and quality of your links.
How to Monitor Your SEO Strategy with Google Search Console
Google Search Console is another free tool by Google. As mentioned earlier, the tool is mostly focused on Technical SEO.
However, you can also use it to check the number of your backlinks.
Note from the Author
I should say that there are definitely a number of tools that are better suited for this task. I am only suggesting Google Search Console because it’s free and it’s fairly straightforward. If you think the tool is too simple, you might want to check SEO Spyglass or Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
How to Check Your Website Links with Google Search Console
To check your website links with Google Search Console:
- Visit https://search.google.com/search-console/about and log in (if you don’t have an account, create one)
- Select the property that you want to monitor
- Scroll down and click on Links
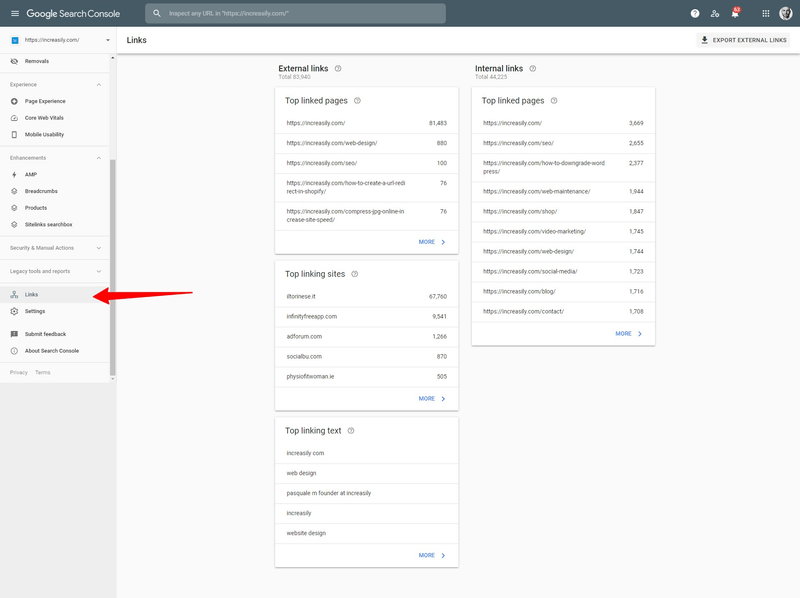
Here you can check the number of both external and internal links by:
- Top Linked Pages
- Top Linking Sites
- Top Linking Text
To export the report, click on Export External Links on the top right of the screen.
How to Monitor Your SEO Strategy with Rank Tracker
![]()
Rank Tracker is another tool from the SEO Powersuite by Link-Assistant. It’s the tool that I use for my website and my clients’.
It’s a very sophisticated yet easy to use tool. At its very basic, you can use to check the keyword ranking for your web pages.
How to Check Your Website Keyword Rankings with Rank Tracker
To check your website keyword rankings with Rank Tracker:
- Visit https://www.link-assistant.com/rank-tracker/ and download Rank Tracker
- Open Rank Tracker and create a new project
- Enter the URL of the website you want to audit
- Enter the keywords you want to monitor your web pages against
- Select the search engines that you want to use
- Run the report
Depending on the settings you chose, you will now see the keyword rankings for your website.
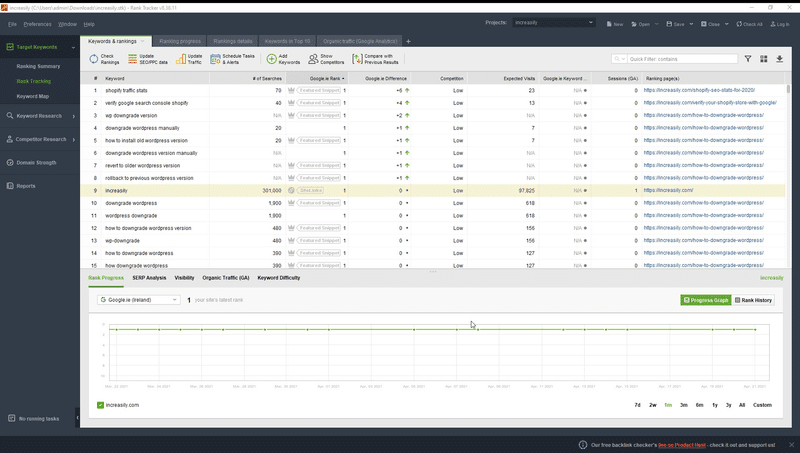
You can download the report by clicking on the appropriate icon on the top right.
SEO Strategy: Conclusion
I hope you liked this article about how to create the perfect SEO strategy.
By no means I consider the article complete but I have tried to put together all the information I know about creating an SEO strategy.
I am sure there is something that I have missed or that I could have written differently about creating an SEO strategy.
If so, please be so kind to let me know.
Finally, thanks so much for making it until the end. I am aware the article is very long and I am thankful that you took the time to read it.
If you want to share it on your social media or bookmark it, feel free to.
Hopefully, you can apply the learnings and principles from this SEO strategy and achieve the success that your website or blog deserves.
Thanks again and keep it up with the great work!
OK, OK, just joking. If you made it this far, you definitely deserve a reward like a free SEO strategy template.
SEO Strategy Bonus: Download the Free SEO Audit Template
Thanks again for reading ‘How to Create the Perfect SEO Strategy in 2022’.
SEO Strategy: Selected Sources
https://www.spyfu.com/blog/seo-goals-to-target-this-year/
https://moz.com/blog/the-6-goals-of-seo-choosing-the-right-ones-for-your-business
https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/seo-analysis-tools
https://www.searchenginejournal.com/seo-audit/technical/?utm_source=sej-feed
https://www.hostgator.com/blog/blogging-helps-seo/
https://ahrefs.com/blog/long-tail-keywords/
https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/content-marketing-plan
https://backlinko.com/seo-strategy
https://www.link-assistant.com/news/google-patents-seo-guide.html
https://www.searchenginejournal.com/topic-clusters-on-site-seo/319109/
SEO Strategy: Images
https://storyset.com/illustration/search-engines/pana
SEO Strategy: Selected Tools
- Upcity Free SEO Report Card
- Seoability
- Woorank
- Seomator
- SEOquake
- Browseo
- The Tech SEO
- Gtmetrix.com
- Pingdom Tools
- Hubspot Website Grader
- Test My Site with Google
- Google Analytics
- Google Search Console
- SEO Powersuite by Link-Assistant
- Asana
- Feedly
- Usetopic Blog Ideas Generator
Comments (2)
Comments are closed.



Balu
28 May 2022Very well explained and thanks for the SEO strategy templates.
Pasquale Mellone
31 May 2022thank you